|
30 October 2025
|
|
|
മലയാളം
|
|
|
|
|
|
Agriculture > Spices
> Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
|
|
|
|
Crop Management
|
|
|
|
Plant Protection
Diseases
Leaf blotch
|
Leaf blotch is caused by Taphrina maculans and appears as small, oval,
rectangular or irregular brown spots on either side of the leaves, which soon become
dirty yellow or dark brown. The leaves also turn yellow. In severe cases
the plants present a scorched appearance and the rhizome yield is reduced.
The fungus is mainly air borne and primary infection occurs on lower leaves with
the inoculum surviving in dried leaves of host, left over in the field. Secondary
infection is most dangerous than primary one causing profuse sprouting all over
the leaves. The fungus persists in summer by means of ascogenous cells on leaf debris,
and desiccated ascospores and blastospores in soil and among fallen leaves
This disease usually appears in October and November. Relative humidity of 80% and
temperatures of 21-23°C favours the primary infection. The disease can be controlled
by spraying mancozeb 0.2%.
|
|
Leaf spot

|
Leaf spot is caused by Colletotrichum capsici and appears as brown spots
of various sizes on the upper surface of the young leaves. The fungus produce
toxic metabolites which cause necrosis on leaves. The spots are irregular in shape
and white or grey in the centre. Later, two or more spots may coalesce and
form an irregular patch covering almost the whole leaf. The affected leaves
eventually dry up. The rhizomes do not develop well.
The disease is usually appears in August and September. It is also observed in November
in certain areas. The disease occurs when there is continuous high humidity in the
atmosphere.
The fungus is carried on the scales of rhizomes which are the source of primary
infection during sowing. The secondary spread is by wind, water and other physical
and biological agents. The same fungus is also reported to cause leaf-spot and fruit
rot of chilli where it is transmitted through seed borne infections. If chilli is
grown in nearby fields or used in crop rotation with turmeric, fungus perpetuates
easily, building up inoculum potential for epiphytotic outbreaks.
The disease can be controlled by spraying mancozeb 0.2% or Bordeaux mixture 1 %.
|
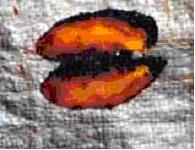
Rhizome rot
|

|
|
The disease is caused by Pythium graminicolum. The collar region
of the pseudo stem becomes soft and water soaked, resulting in collapse of the plant
and decay of rhizomes. Treating the seed rhizomes with mancozeb 0.3% for 30
minutes prior to storage and at the time of sowing prevents the disease. When
the disease is noticed in the field, drench the soil with Cheshunt compound or 1%
bordeaux mixture.
|
Nematode pests

|
Root knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) and burrowing nematode (Radopholus
similis) are the two important nematodes causing damage to turmeric.
Root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) are of common occurrence in Andhra
Pradesh. Wherever nematode problems are common, use only healthy, nematode-free
planting material. Increasing the organic content of the soil also checks
the multiplication of nematodes.
|
Insect pests
Shoot borer
|
The shoot borer (Conogethes punctiferalis) is the most serious pest of
turmeric. The larvae bore into pseudostems and feed on internal tissues. The
presence of a borehole on the pseudostem through which frass is extruded and the
withered central shoot is a characteristic symptom of pest infestation. The
adult is a medium sized moth with a wingspan of about 20 mm; the wings are orange-yellow
with minute black spots. Fully-grown larvae are light brown with sparse hairs.
Spraying malathion 0.1% or monocrotophos 0.075% at 21 day intervals during July
to October is effective in controlling the pest infestation. The spraying
has to be initiated when the first symptom of pest attack is seen on the inner most
leaf. Shoot borers can be controlled by spraying 0.05% dimethoate or 0.05% quinalphos.
|
|
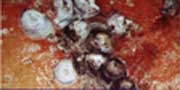
Rhizome scale
|
The rhizome scale (Aspidiella hartii) infests rhizomes in the field (at
later stages of the crop) and in storage. Adult (female) scales are circular
(about 1 mm diameter) and light brown to grey and appear as encrustations
on the rhizomes. They feed on sap and when the rhizomes are severely infested, they
become shrivelled and desiccated affecting its germination. Treat seed material
with quinalphos 0.075% (for 20-30 minutes) before storage and also before sowing
in case the infestation persists. Discard and do not store severely infested
rhizomes.
|
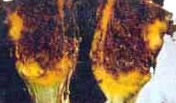
Rhizome fly
|
Rhizome flies are black and ant like and lay eggs at the base of the stem. This
pest appears from the beginning of October to till the crop is harvested. This pest
also infests rhizome rot-affected-rhizomes. After hatching, the flies penetrate
into rhizomes and feed the internal content completely.The yield loss due to this
pest is 48-50%. Use disease free rhizomes.
|

|
|
Minor pests
Adults and larvae of leaf feeding beetles such as Lema spp. feed on leaves
especially during the monsoon season and form elongated parallel feeding marks on
them. The spraying of malathion 0.1 % undertaken for the management of shoot
borer is sufficient to manage this pest.
The lacewing bug (Stephanitis typicus) infests the foliage causing them
to turn pale and dry up. The pest infestation is more common during the post-monsoon
period especially in drier regions of the country. Spraying dimethoate (0.05%
) is effective in managing the pest.
The turmeric thrip (Panchaetothrips indicus) infests the leaves causing
them to roll, turn pale and gradually dry up. The pest infestation is more
common during the post monsoon period especially in drier regions of the country.
Spraying dimethoate 0.05%, is effective for the management of the pest.
|
|
|
|
Top
|
|
|
|
|
|